Early Signs You Should Seek Professional Care for a Knee Injury
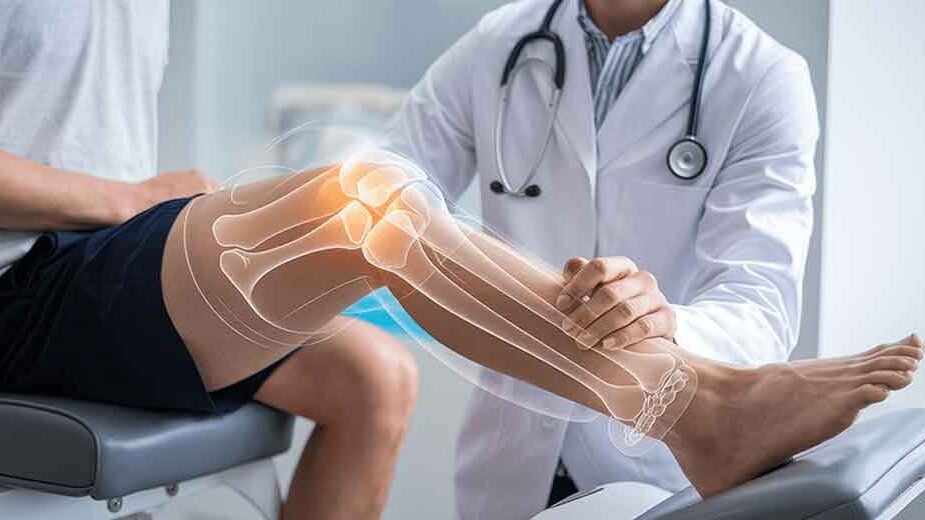
Knee injuries can affect people of all ages and activity levels, from athletes to those who experience everyday wear and tear. While minor discomfort or soreness often resolves with rest and self-care, certain symptoms warrant prompt professional attention. Ignoring these warning signs can lead to long-term complications, decreased mobility, and persistent pain. We will explore the early indicators that suggest a knee injury requires professional evaluation, helping individuals act quickly to prevent further damage and ensure proper recovery. Recognizing these signals early can significantly improve joint health and overall quality of life.
Recognizing the Warning Signs of Knee Injury
- Persistent Pain and Swelling
Experiencing ongoing knee pain that does not improve with rest, ice, or over-the-counter medications is a clear indication to seek professional knee injury care in Houston. Swelling that appears suddenly or increases over time can indicate internal damage, such as ligament tears, cartilage injury, or meniscus problems. Pain may occur during specific movements, such as bending, climbing stairs, or squatting, or it may be present even at rest. Additionally, a warm sensation around the joint or visible redness may indicate inflammation or fluid accumulation, both of which warrant assessment. Ignoring persistent pain and swelling can worsen the injury, leading to chronic problems or difficulty in performing daily activities. Prompt evaluation ensures that an appropriate diagnosis is made, and treatment can begin before complications arise.
- Difficulty Bearing Weight or Instability
If standing, walking, or bearing weight on the affected knee causes discomfort, weakness, or a sensation of the knee giving way, professional attention is necessary. Instability can indicate damage to ligaments that provide structural support, such as the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) or medial collateral ligament (MCL). Even minor instability can compromise joint function over time, increasing the risk of falls or further injury. Patients may experience a sudden loss of strength or coordination, which can make routine movements difficult. Early evaluation enables clinicians to determine the severity of ligament or tendon involvement and to recommend targeted interventions, such as bracing, therapy, or surgical options, when necessary. Addressing instability promptly helps maintain mobility and prevents worsening joint damage.
- Locking or Catching Sensations
A knee that locks, catches, or clicks during movement may indicate a meniscus tear or loose cartilage fragments within the joint. These mechanical symptoms often worsen with activities such as bending, squatting, or twisting. A sudden inability to fully extend or flex the knee can interfere with normal walking patterns and daily activities. These symptoms rarely resolve without intervention and may require imaging or arthroscopic procedures to identify the underlying issue. Professional care ensures that the joint is properly assessed, minimizing the risk of further cartilage damage and preserving long-term knee function. Ignoring these sensations can lead to chronic joint problems, persistent pain, and decreased range of motion.
- Sudden or Severe Injury
Acute trauma to the knee from falls, sports, or accidents should always be evaluated promptly. Sudden injuries may involve fractures, ligament tears, or dislocations, which can have immediate and severe consequences if left untreated. Even if the pain initially seems manageable, underlying structural damage can worsen without timely intervention. Early professional evaluation often includes diagnostic imaging and thorough examination, guiding treatment decisions such as immobilization, rehabilitation, or surgery. Immediate care following a severe knee injury reduces the risk of long-term disability, ensures proper alignment of bones and tissues, and improves overall recovery outcomes.
- Persistent Stiffness and Limited Range of Motion
Difficulty bending or straightening the knee, accompanied by stiffness or discomfort, signals potential joint damage or inflammation. Persistent stiffness may indicate conditions like arthritis, tendinitis, or cartilage degeneration, which require professional assessment. Delayed treatment can result in decreased flexibility, muscle weakness, and impaired mobility. Regular daily activities such as sitting, standing, or climbing stairs may become increasingly difficult. Consulting a professional enables an accurate diagnosis and the development of a structured rehabilitation plan, including physical therapy exercises or interventions to restore the range of motion and reduce pain. Early attention helps prevent progressive joint dysfunction and maintains overall knee health.
- Bruising or Visible Deformity
The presence of significant bruising, swelling, or abnormal appearance in the knee after trauma is a clear indication to seek medical care. Visible changes, such as misalignment, unusual protrusions, or uneven swelling, may indicate fractures, dislocations, or severe ligament injuries. Immediate evaluation helps determine the extent of the damage and prevents further complications. In some cases, these injuries may require immobilization, corrective procedures, or surgical intervention. Prompt assessment helps ensure that the joint heals properly, reducing the risk of chronic pain or permanent deformity. Recognizing early signs allows patients to take proactive steps to protect their knees and maintain function.
- Recurring Pain After Activity
Experiencing recurrent knee pain after physical activity, even if initially mild, may indicate overuse injuries or early degeneration. Athletes and active individuals often overlook discomfort, attributing it to routine exertion. However, recurring pain may indicate tendonitis, bursitis, or stress-related injuries that worsen without intervention. Professional evaluation guides appropriate rest, activity modifications, or targeted exercises to support recovery. Addressing recurring pain early helps prevent chronic conditions, preserves athletic performance, and ensures the knee remains functional for daily activities. Ignoring repeated discomfort may lead to persistent pain, reduced mobility, and long-term joint problems.
Recognizing the early signs of knee injury and seeking professional care is crucial for long-term joint health. Persistent pain, swelling, instability, mechanical symptoms, acute trauma, stiffness, visible deformities, recurring pain, and abnormal sounds all indicate the need for evaluation. Addressing these warning signals promptly helps prevent complications, preserves mobility, and supports effective recovery. Timely intervention enables accurate diagnosis, appropriate treatment plans, and improved outcomes, thereby ensuring that individuals maintain an active, pain-free lifestyle. Paying attention to these early indicators empowers patients to protect their knees and invest in their long-term well-being.
Last modified: December 17, 2025